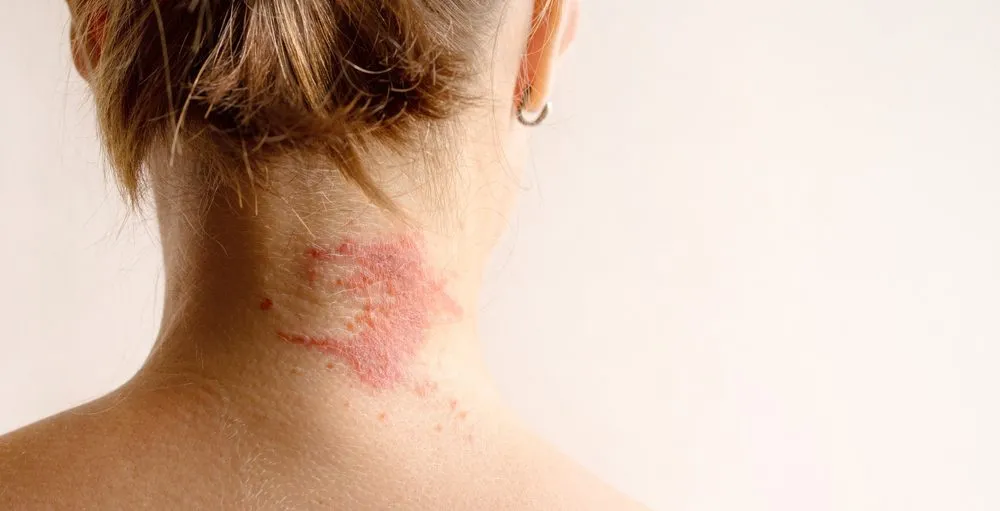
Eczema
Eczema is a common skin condition that affects millions of people, ranging from infants to adults. It often manifests as patches of inflamed, itchy, and sometimes painful skin. While the symptoms may seem similar, there are different types of eczema, each with its own triggers and characteristics. Understanding these types can be a helpful step in managing the condition and knowing when to consult a dermatologist.
Understanding Eczema
Eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, is a chronic skin condition that causes the skin to become red, inflamed, and itchy. While its exact cause is unknown, it is believed to result from a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Eczema is not contagious, but it can be uncomfortable and sometimes interfere with daily life due to persistent itching and irritation.
Types of Eczema and Their Symptoms
Understanding the different types of eczema and their associated symptoms is the first step in managing the condition effectively. Recognizing the specific characteristics of your eczema can help in identifying triggers, choosing the right treatment options, and improving overall skin health. By learning to distinguish between the various forms of eczema, individuals can take a proactive approach to reducing flare-ups and improving their quality of life.
Atopic Dermatitis
Atopic dermatitis is the most common form of eczema and typically begins in childhood. It is often associated with other allergic conditions such as asthma or hay fever.
Symptoms include:
- Dry, scaly skin
- Red or brown patches, especially on the hands, feet, ankles, wrists, neck, and around the elbows or knees
- Intense itching, particularly at night
- Cracking or weeping skin in severe cases
Contact Dermatitis
Contact dermatitis occurs when the skin reacts to a substance it has been exposed to. This could be caused by irritants such as soaps, detergents, or cosmetics, or allergens like poison ivy or nickel.
Symptoms include:
- Red, itchy rash
- Blisters or bumps in some cases
- Cracked or dry skin
- Burning or stinging sensation
Dyshidrotic Eczema
This type of eczema is characterized by small, fluid-filled blisters that typically form on the hands and feet. It may be triggered by stress, allergens, or moist conditions.
Symptoms include:
- Blisters that itch or cause a burning sensation
- Cracked or scaly skin as the blisters heal
- Painful skin in severe cases
Nummular Eczema
Nummular eczema appears as circular, coin-shaped spots on the skin. It is often triggered by dry skin, insect bites, or contact with allergens.
Symptoms include:
- Round spots of irritated skin, often itchy or scaly
- Reddish or brownish patches
- Oozing or crusting in more severe cases
Seborrheic Dermatitis
Seborrheic dermatitis commonly affects areas of the body with a high concentration of oil-producing glands, such as the scalp, face, and upper chest.
Symptoms include:
- Red, greasy patches of skin
- Yellow or white scales on the surface of the skin
- Persistent itching or irritation
- Flaking skin, commonly referred to as dandruff when it occurs on the scalp
Stasis Dermatitis
Stasis dermatitis typically develops in individuals with poor circulation, often affecting the lower legs. It is commonly associated with conditions such as varicose veins or other circulatory issues.
Symptoms include:
- Swollen legs, especially after long periods of standing or sitting
- Red, itchy, and inflamed skin on the lower legs
- Dry, cracked skin
- Development of ulcers in severe cases
Managing Eczema
While there is no known cure for eczema, there are a variety of treatments and lifestyle changes that help manage symptoms and prevent flare-ups. Maintaining a good skincare routine with gentle, fragrance-free products can significantly reduce irritation. It’s also key to identify and avoid potential triggers, whether they are allergens, irritants, or specific environmental factors such as extreme temperatures or stress. Over-the-counter topical treatments, such as hydrocortisone creams, can provide temporary relief for mild symptoms, while prescription medications may be necessary for more severe cases.
For personalized advice, consult a dermatologist who will recommend a tailored treatment plan. Addressing eczema early and consistently can help minimize discomfort and improve overall quality of life.
Help from an Expert
A dermatologist will not only provide professional guidance but also pinpoint specific triggers causing your eczema. They may suggest treatments such as medicated creams, oral medications, or therapies like phototherapy, depending on the severity of your condition. Regular check-ins with an expert allow for your treatment to be adjusted as needed, keeping your symptoms under control and helping you manage flare-ups effectively. Don’t hesitate to seek expert support—early intervention can make a big difference.
Discover the latest news and updates on The Blog Verge






